Spring3.2 AOP个人分析: AOP, 即Aspect-Oriented-Programming, 面向切面编程, 又一Spring的核心,被广泛应用,如在Spring-tx中都有用到,其
Spring3.2 AOP个人分析:
AOP, 即Aspect-Oriented-Programming, 面向切面编程, 又一Spring的核心,被广泛应用,如在Spring-tx中都有用到,其好处是实现松耦合的外围处理程序,先说些理论吧。
- 切面(Aspect): 一种模块化机制,用来描述分散在对象,类或函数中的横切关注点,它主要用于处理一些特定功能,而并不是业务逻辑,比如,日志处理,事务处理等,既然不是业务逻辑,就应该和业务逻辑代码分开,因此比较好的解决办法就是使用切面来编程,对业务代码破坏小,而且易于单独维护。
- 通知(Advice): 定义在目标点干什么,比如在方法调用前,方法调用后等,Spring对AOP Alliance定义的Advice接口作了自己的扩展,如图:

例如其中BeforeAdvice的扩展接口MethodBeforeAdvice, 及该通知会在目标对象的目标方法调用之前被调用:
public interface MethodBeforeAdvice extends BeforeAdvice { void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable;}public class CountingBeforeAdvice extends MethodCounter implements MethodBeforeAdvice { @Override public void before(Method m, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { count(m); }public class MethodCounter implements Serializable { private HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); private int allCount; protected void count(Method m) { count(m.getName()); } protected void count(String methodName) { Integer i = map.get(methodName); i = (i != null) ? new Integer(i.intValue() + 1) : new Integer(1); map.put(methodName, i); ++allCount; } ...}- 切入点(Pointcut): 定义通知应该作用于哪些目标方法,可以进行一些方法匹配配置,看看spring中PointCut体系:

看其中的AbstractRegexpMethodPointcut,它有一个模版方法matchesPatterns, 就是先匹配包括的方法,再匹配不包括的方法,都由子类来实现,如JdkRegexpMethodPointcut的实现。
protected boolean matchesPattern(String signatureString) { for (int i = 0; i < this.patterns.length; i++) { boolean matched = matches(signatureString, i); if (matched) { for (int j = 0; j < this.excludedPatterns.length; j++) { boolean excluded = matchesExclusion(signatureString, j); if (excluded) { return false; } } return true; } } return false;}对应JdkRegexpMethodPointcut的实现:
protected boolean matches(String pattern, int patternIndex) { Matcher matcher = this.compiledPatterns[patternIndex].matcher(pattern); return matcher.matches();}protected boolean matchesExclusion(String candidate, int patternIndex) { Matcher matcher = this.compiledExclusionPatterns[patternIndex].matcher(candidate); return matcher.matches();}- Advisor(通知器):Advice(处理程序)和Pointcut(处理程序进入点)完成后,我们还要一个管理者来管理它们,这就是Advisor:

到此将了aop中的几个重要组件概念,接下来是如何实现aop。
这就要涉及到核心的ProxyFactoryBean了:
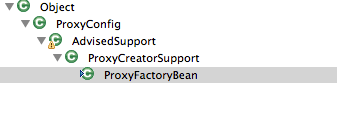
那么ProxyFactoryBean是怎么来产生代理对象的呢,如下:
public Object getObject() throws BeansException { initializeAdvisorChain(); //初始化通知链, 为Proxy代理对象配置Advisor链 if (isSingleton()) { return getSingletonInstance(); } else { if (this.targetName == null) { logger.warn("Using non-singleton proxies with singleton targets is often undesirable. " + "Enable prototype proxies by setting the 'targetName' property."); } return newPrototypeInstance(); }}看看initializeAdvisorChain方法:
private synchronized void initializeAdvisorChain() throws AopConfigException, BeansException { if (this.advisorChainInitialized) { //如果已经初始化了,就返回 return; } if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptorNames)) { ... // Materialize interceptor chain from bean names. for (String name : this.interceptorNames) { //这个interceptorNames是我们xml中配置的通知器(拦截器)bean的name if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Configuring advisor or advice '" + name + "'"); } if (name.endsWith(GLOBAL_SUFFIX)) { ... else { // If we get here, we need to add a named interceptor. // We must check if it's a singleton or prototype. Object advice; if (this.singleton || this.beanFactory.isSingleton(name)) { // Add the real Advisor/Advice to the chain. advice = this.beanFactory.getBean(name); } else { // It's a prototype Advice or Advisor: replace with a prototype. // Avoid unnecessary creation of prototype bean just for advisor chain initialization. advice = new PrototypePlaceholderAdvisor(name); } addAdvisorOnChainCreation(advice, name); } } } this.advisorChainInitialized = true;}private synchronized Object getSingletonInstance() { if (this.singletonInstance == null) { this.targetSource = freshTargetSource(); if (this.autodetectInterfaces && getProxiedInterfaces().length == 0 && !isProxyTargetClass()) { // Rely on AOP infrastructure to tell us what interfaces to proxy. Class targetClass = getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException("Cannot determine target class for proxy"); } setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetClass, this.proxyClassLoader)); } // Initialize the shared singleton instance. super.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); this.singletonInstance = getProxy(createAopProxy()); //这里就通过createAopProxy来创建我们的代理对象了 } return this.singletonInstance;}public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); // 这里获取xml中配置的目标对象 if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface()) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return CglibProxyFactory.createCglibProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); }}JdkDynamicAopProxy是内部怎么创建代理对象的呢?
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } Class[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);}JdkDynamicAopProxy实现了JDK动态代理的标准接口InvocationHandler,当我们调用目标代理对象时会直接调用invoke方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { ... List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);//获取拦截器链 // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does // nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying. retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args); //没有拦截器就直接调用目标对象的目标方法 } else { // We need to create a method invocation... //有拦截器则先处理拦截器 invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } ...}public Object proceed() throws Throwable { //We start with an index of -1 and increment early. if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); //真正调用我们的目标对象的对应方法了 } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); //调用拦截器处理方法 } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. return proceed(); //继续处理下一个拦截器 } } else { // It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have // been evaluated statically before this object was constructed. return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); }}这就是JdkDynamicAopProxy生成目标代理对象的实现过程,那么cglib怎么实现的呢,看DynamicAdvisedIntercept的intercept方法:
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { ... target = getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, args); //没有配置拦截器 } else { // We need to create a method invocation... retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); //拦截器链处理 } retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal;}至此,简单讲解了Spring Aop代理对象的实现过程。
说了这么多,还是要得有个demo才行, 这里我们会对目标对象建立一条具有2个拦截器的拦截链:
- 一个后置通知:
package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;/** * 定制的后置通知,用于注入Advisor */public class MyAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice{ @Override public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("I am MyAdvice, invoked after target method return."); }}- 一个普通的方法拦截器:
package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;/** * Advisor Test Class */public class MyInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("I am MyInterceptor, invoked before target method execute."); return invocation.proceed(); }}- 一个jdk正则表达式匹配的切入点:
package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;import org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut;/** * 定制的PointCut, 用于注入Advisor * */public class MyPointCut extends JdkRegexpMethodPointcut { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;}- 一个管理切入点和通知(拦截器)的通知器:
package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;/** * 定制的通知器 */public class MyAdvisor extends DefaultPointcutAdvisor { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; }- 需要代理的目标接口及其实现:
package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;public interface MyService { public void helloAop();}package org.spring.framework.learn.aop;public class MyServiceImpl implements MyService{ public void helloAop(){ System.out.println("This is a target for aop handle."); }}- 当然还有spring的配置文件aop-test.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd"><beans> <!-- 定制后置通知,并注入到Advisor中 --> <bean id="myAdvice" class="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyAdvice" /> <!-- 定制切入点, 匹配方法,并注入到Advisor --> <bean id="myPointCut" class="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyPointCut"> <property name="pattern" value="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyServiceImpl.*" /> </bean> <!-- 定制Advisor, 用于对目标对象实现扩展 --> <bean id="myAdvisor" class="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyAdvisor"> <!-- 通知 --> <property name="advice"> <ref bean="myAdvice"/> </property> <!-- 切点 --> <property name="pointcut"> <ref bean="myPointCut"/> </property> </bean> <!-- 拦截器用于拦截目标对象,也用于对象增强 --> <bean id="myInterceptor" class="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyInterceptor"/> <!-- 代理对象配置 --> <bean id="myAopProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="proxyInterfaces"> <value>org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyService</value> </property> <property name="target"> <bean class="org.spring.framework.learn.aop.MyServiceImpl"></bean> </property> <!-- --> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>myInterceptor</value> <value>myAdvisor</value> </list> </property> </bean></beans>- 测试用例:
public class ProxyFactoryBeanTests { private static ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("configs/aop-test.xml"); @Test public void testProxyFactoryBean1(){ MyService in = (MyService)context.getBean("myAopProxy"); in.helloAop(); }}- 运行结果:
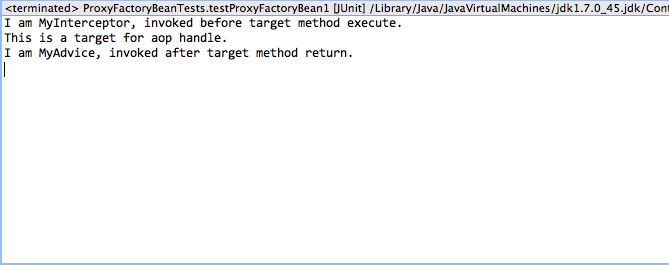
收工,不懂留话。




